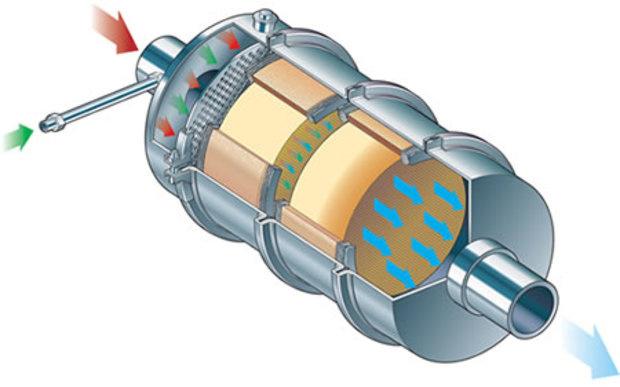
The automotive industry's compliance with the world's toughest emission laws hinges on a complex chemical process happening in a canister underneath vehicles. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology has become a multi-billion-dollar field of intense competition and innovation. With the future of internal combustion at stake, suppliers and OEMs are investing billions to perfect this technology, making it more effective, affordable, and crucial for the diesel engine's license to operate in a decarbonizing world.
This strategic importance is reflected in its financial trajectory. According to Straits Research, the global automotive selective catalytic reduction (SCR) sector was valued at USD 11.83 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach from USD 13.22 billion in 2025 to USD 32.28 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.8% during the forecast period (2025-2033). This growth is underpinned by the technology's non-negotiable role in meeting a complex web of global regulations.
Analysis of a High-Stakes Competitive Arena
The key players are executing distinct strategies based on their core competencies, from hardware to chemistry.
-
The Integrated System Suppliers: Companies like Bosch (Germany) and Continental (Germany) are competing to provide the entire aftertreatment "recipe" – the dosing control unit, injectors, sensors, and the catalyst canister itself. Their analysis shows a focus on creating proprietary, closed-loop systems that offer OEMs a seamless, warranty-backed solution. Bosch's recent advancements in AI-powered dosing control exemplify this, using real-time data to maximize NOx conversion while minimizing DEF consumption.
-
The Catalyst Specialists: BASF (Germany) and Johnson Matthey (UK) compete at the molecular level. Their battle is over catalyst formulation patents and creating materials that deliver peak performance over a vehicle's entire lifespan. A key update from this segment is the development of iron-zeolite catalysts as a more cost-effective and thermally durable alternative to traditional copper-zeolite formulations for certain applications.
-
OEM In-House Development: Major truck manufacturers like Daimler Truck AG (Germany) and Volvo Group (Sweden) are increasingly bringing core aftertreatment expertise in-house to gain a competitive edge and control costs. Daimler's recent unveiling of its new DT12 Powertrain highlighted a fully integrated SCR system designed specifically for its platform, promising superior efficiency and reliability.
-
Regional Champions and the DEF Ecosystem: In Asia, companies like China Automotive Systems Group are developing cost-competitive SCR systems for the massive domestic market. The growth of the sector also fuels ancillary industries. CF Industries (USA) and Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO) are expanding their DEF production capacity, understanding that the availability of high-quality reductant is critical for the technology's success and widespread adoption.
Global Trends and Regional Regulatory Drivers
The development of SCR technology is not uniform; it is shaped by regional policies and broader industry shifts.
-
The Euro 7 Preoccupation: In Europe, the upcoming Euro 7 standards are the primary driver of innovation. These rules will require near-zero NOx emissions under virtually all driving conditions, pushing for SCR systems that work efficiently from a cold start. This has accelerated research into electrically heated catalysts and close-coupled SCR systems placed nearer to the engine.
-
The Dual Strategy: Diesel and Biofuels: SCR technology is being adapted for use with renewable fuels like biodiesel and hydrogenated vegetable oil (HVO). Research is focused on ensuring catalyst longevity and performance with these alternative fuels, which produce different exhaust gas compositions than standard diesel.
-
The Commercial Vehicle Lifeline: While the passenger car segment electrifies, the path to zero-emission long-haul trucking is longer. This makes SCR technology absolutely vital for the commercial vehicle industry for the next two decades. Investments here are focused on extreme durability, low operational costs, and maximum reliability for million-mile lifespans.
Recent News and Strategic Moves
The industry is constantly evolving. A major recent news item was Faurecia (France), part of Forvia, launching a new compact aftertreatment system designed for urban commercial vehicles, addressing packaging constraints in smaller trucks. In a significant consolidation move, Tenneco (USA) completed its acquisition of Federal-Mogul, further integrating exhaust and powertrain expertise. Meanwhile, in India, Bharat Stage VI (BS6) Phase 2 regulations have come into force, forcing OEMs like Tata Motors and Ashok Leyland to adopt even more advanced SCR systems with sophisticated OBD, creating a boom for suppliers in the region.
In summary, the automotive SCR sector is a critical and high-growth engineering battlefield. Defined by the interplay of stringent global regulations, fierce competition between tech suppliers, and the enduring need for clean diesel power, particularly in commercial transport, its evolution is key to the industry's environmental credentials.