In industrial processes across manufacturing, petrochemical, power generation, and HVAC sectors, thermal management stands as a critical factor in operational success. Among the various heat transfer solutions available, the shell and tube heat exchanger remains the most widely adopted technology due to its proven reliability, versatility, and efficiency. These robust systems facilitate heat transfer between two fluids while keeping them separated, making them indispensable for applications ranging from crude oil refining to pharmaceutical production. Understanding how to maximize their efficiency can lead to significant energy savings, reduced operational costs, and improved process performance.
Understanding Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design
The fundamental design of shell and tube heat exchangers consists of a series of tubes housed within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows through the tubes while another flows around them within the shell, allowing heat transfer through the tube walls. This seemingly simple configuration offers remarkable flexibility through variations in tube arrangement, baffle design, and flow patterns.
The effectiveness of these systems depends heavily on several design parameters. The number of tube passes, shell passes, and the arrangement of baffles all influence heat transfer rates and pressure drops. Single-pass designs offer simplicity, while multi-pass configurations can dramatically improve heat transfer coefficients at the cost of increased pressure drop. Engineers must carefully balance these factors based on specific application requirements.
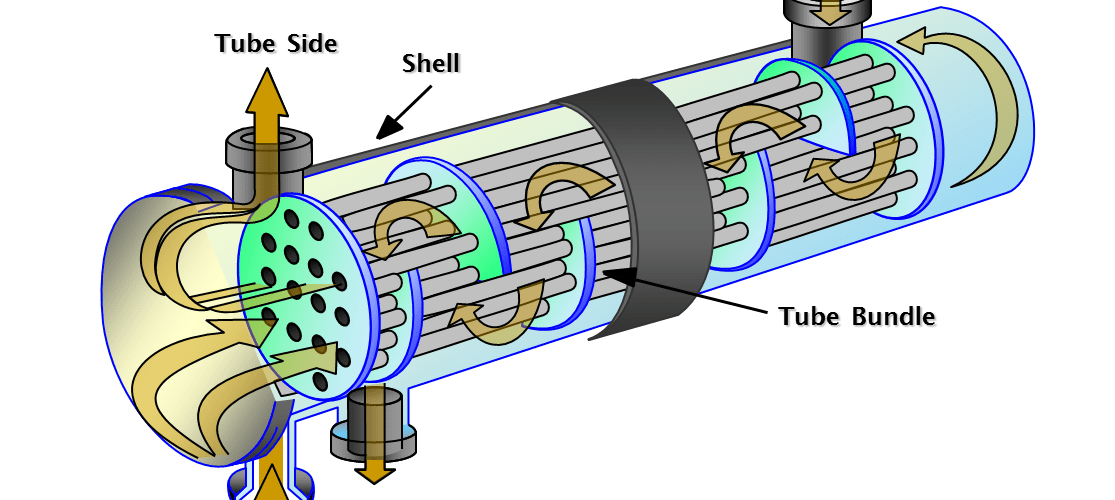
Key Factors Affecting Heat Exchanger Efficiency
Flow Configuration and Velocity
The flow arrangement—whether counter-current, co-current, or cross-flow—significantly impacts thermal performance. Counter-current flow, where fluids move in opposite directions, typically provides the highest efficiency by maintaining a more consistent temperature difference along the exchanger length. Optimizing fluid velocities ensures turbulent flow conditions that enhance heat transfer while avoiding excessive pressure drops that increase pumping costs.
Fouling Prevention and Maintenance
Fouling represents one of the most significant challenges to maintaining peak efficiency. Deposits from scale, biological growth, corrosion products, or particulate matter create insulating layers that severely impair heat transfer. Regular cleaning schedules, proper filtration, chemical treatment programs, and selecting appropriate materials can minimize fouling effects. Some operations benefit from designing exchangers with higher initial surface areas to accommodate gradual fouling between maintenance cycles.
Material Selection
The choice of construction materials affects both thermal conductivity and longevity. Copper alloys offer excellent heat transfer characteristics for many applications, while stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance in aggressive environments. Titanium excels in highly corrosive conditions despite higher initial costs. Matching materials to process fluids prevents degradation that compromises efficiency over time.
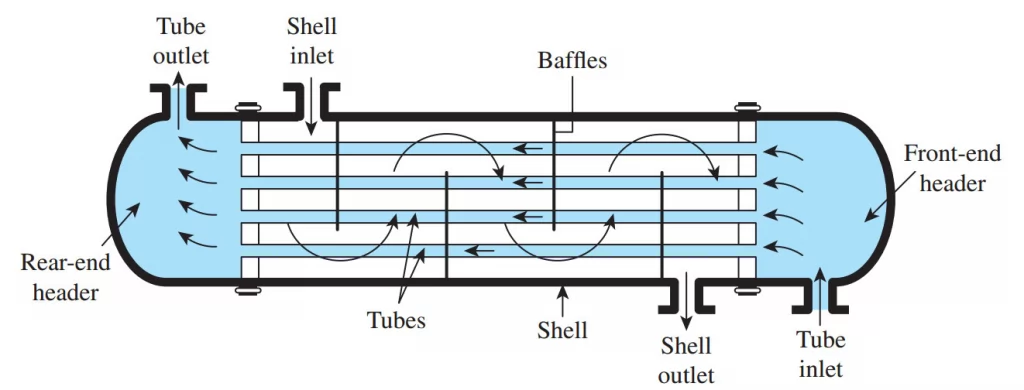
Operational Strategies for Enhanced Performance
Temperature and Pressure Optimization
Operating parameters must align with design specifications to achieve maximum efficiency. Running at temperatures significantly below design points wastes potential, while exceeding limits risks equipment damage. Monitoring temperature differentials between inlet and outlet streams helps identify declining performance before it becomes critical.
Flow Rate Management
Maintaining proper flow rates on both shell and tube sides ensures optimal heat transfer coefficients. Flow rates too low result in laminar conditions with poor heat transfer, while excessive rates cause unnecessary pressure drops and potential erosion. Variable frequency drives on pumps allow fine-tuning of flow rates as process conditions change.
Baffle Configuration
Baffles serve dual purposes: supporting tubes and directing shell-side flow to enhance turbulence. Baffle spacing, cut size, and orientation influence both heat transfer rates and pressure drops. Some applications benefit from segmental baffles, while others perform better with helical or rod baffles that reduce pressure drop while maintaining good heat transfer.
Advanced Efficiency Enhancement Techniques
Tube Enhancement Technologies
Modern enhancement techniques can boost performance beyond conventional smooth-tube designs. Internally finned tubes, twisted tape inserts, and specially profiled surfaces increase turbulence and heat transfer area. These modifications can increase heat transfer coefficients by 50-200% in suitable applications, often allowing smaller exchanger footprints or improved capacity from existing units.
Heat Transfer Augmentation
Strategic placement of turbulence promoters, spiral wires, or corrugated tubes disrupts boundary layers where thermal resistance concentrates. While these features increase pressure drop, the efficiency gains often justify the additional pumping costs, particularly in applications with high-value heat recovery potential.
Process Integration
Examining heat exchangers within the broader process context reveals optimization opportunities. Heat integration studies identify where waste heat from one process stream can preheat another, reducing overall energy consumption. Pinch analysis methodologies help identify optimal temperature approaches and minimum energy requirements.

Monitoring and Performance Assessment
Implementing continuous monitoring systems enables proactive efficiency management. Temperature sensors, pressure transmitters, and flow meters provide real-time performance data. Tracking overall heat transfer coefficients over time reveals fouling trends, allowing scheduled cleaning before efficiency drops significantly. Advanced analytics can predict maintenance needs and optimize cleaning schedules based on actual performance degradation rather than arbitrary time intervals.
Regular performance testing against design specifications identifies efficiency losses. Comparing actual duty to design duty highlights problems requiring attention. Heat transfer calculations using measured temperatures and flow rates quantify current performance and establish benchmarks for improvement initiatives.
Partner with Industry Leaders for Optimal Heat Transfer Solutions
When it comes to maximizing the efficiency and reliability of your thermal management systems, working with experienced manufacturers makes a significant difference. Companies like Kinetic Engineering specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance heat exchangers tailored to specific industrial applications. Their comprehensive product line includes not only traditional shell and tube configurations but also specialized solutions like finned tube heat exchangers that provide enhanced heat transfer for demanding applications.
Kinetic Engineering's expertise in thermal engineering ensures that each system is optimized for the unique requirements of your process, whether you need compact designs for space-constrained installations or robust units for harsh operating environments. Their shell and tube heat exchangers are built to stringent quality standards, incorporating the latest design innovations to deliver superior performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Maximizing efficiency with shell and tube heat exchangers requires a comprehensive approach that addresses design parameters, operational practices, maintenance strategies, and continuous monitoring. By understanding the factors that influence performance and implementing proven optimization techniques, industrial facilities can achieve significant energy savings while improving process reliability. Whether upgrading existing systems or specifying new equipment, attention to these efficiency principles delivers measurable returns through reduced operating costs and enhanced productivity. As energy costs continue rising and environmental regulations tighten, the importance of efficient heat transfer systems will only grow, making optimization efforts increasingly valuable for competitive industrial operations.



